RBAC访问控制实验
RBAC简介
RBAC(Role-based Access Control)基于角色的访问控制模型,从根本上来讲是解决资源的控制的问题,而在这里所提出的解决方案是who、what以及how的解决方式,其中who是指权限的拥有者或者主体(user,role)而what就是资源或者对象,可以抽象为who对what进行来how操作
RBAC其实是一种分析模型,主要分为:基本模型RBAC0(Core RBAC)、角色分层模型RBAC1(Hierarchal RBAC)、角色限制模型RBAC2(Constraint RBAC)和统一模型RBAC3(Combines RBAC)。
RBAC0
由四部分组成:用户、角色、会话和许可,
RBAC1(角色分层模型)
在RBAC0的基础上引入了角色的继承,使得角色具有了上下级的关系,例如下图
RBAC2(约束模型)
加入了约束的概念,并且引入了静态职责分离SSD(Static Separation of Duty)和动态职责分离DSD(Dynamic Separation of Duty)
SSD是用户和角色的指派阶段加入的,主要是对用户和角色有如下约束:
- a、互斥角色:同一个用户在两个互斥角色中只能选择一个
- b、基数约束:一个用户拥有的角色是有限的,一个角色拥有的许可也是有限的
- c、先决条件约束:用户想要获得高级角色,首先必须拥有低级角色
DSD是会话和角色之间的约束,可以动态的约束用户拥有的角色,如一个用户可以拥有两个角色,但是运行时只能激活一个角色。
RBAC3(RBAC1 + RBAC2)
实验内容
原始框架
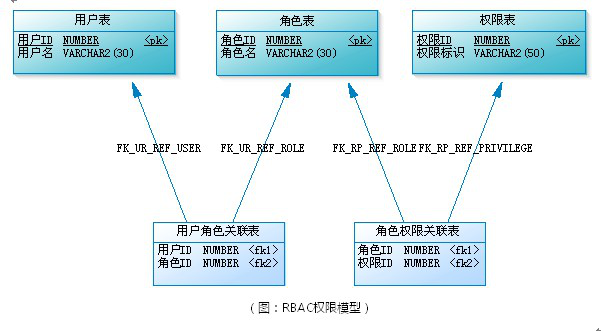
主体、角色、权限的定义以及相应配置
在这个例子当中,主体/用户是A、B、M1、C、D、M2以及BOSS,而相应的角色分为了第一类员工(A、B),部门经理(M1),第二类员工(C、D),经理(M2)以及BOSS,对应的权限就是读取,执行;读取、删除、执行;新建、读取、更改;新建、删除、读取、更改;所有权限
注意事项
在运行的本文件的时候,管理员账户密码为1234
其次,我参考了一些网上方法,采用的是数据库的格式,所以每次运行完的结果都会存在对应的db文件中,可以通过新建txt并且重新命名为datatable.db来重新初始化
最后,由于是花了几天时间实现的,所以不同地方的注释和print出来的东西有中文有英文,但是都是自己验证通过的
设计文档
设计思路:
在这里我希望采用三个对象来对于用户、角色还有权限进行分别管理,同时,我才用了sqlite包来帮助实现对应的db文件中的几个表,而对于用户/角色/权限的一些操作,是通过这三个类里面的函数来进行实现的,下面来对不同的类进行分别解释
对用户管理的类usermanager()
包含的方法以及所要完成的功能/作用:
函数 函数的功能/作用 set_user_table() 初始化对应的user表,实现例子里面的内容 set_user_role_table() 初始化对应的用户角色关联表 add_user_role() 这是在添加用户的时候所需要用到的,要了解想要添加的用户的角色id user_info() 获取所要添加的用户的名称以及用户id add_user() 在用户表里面检索,符合要求时添加对应的表项 user_name_show() 显示用户的信息的时候用到的 具体代码实现
import sqlite3 #初始化对于用户管理的类 class usermanager(): def __init__(self): super().__init__() #该方法用于设置对应的用户表 def set_user_table(self): #建立连接和游标对象 con = sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db") cur = con.cursor() sql = 'insert into user(user_name,user_id) values(?,?)' try: cur.executemany(sql,[("员工A",1),("员工B",2),("员工C",3),("员工D",4),("部门经理M1",5),("部门经理M2",6),("Boss",7)]) con.commit() print("用户表设置成功") except Exception as e: print(e) con.rollback() print("设置用户表失败") finally: cur.close() con.close() #该方法用于设置对应的用户角色关联表 def set_user_role_table(self): con=sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db") cur=con.cursor() sql='insert into user_role(user_id,role_id) values(?,?)' try: cur.executemany(sql,[(1,101),(2,101),(3,201),(4,201),(5,100),(6,200),(7,404)]) con.commit() print("用户角色关联表设置成功") except Exception as e: print(e) con.rollback() print("用户角色关联表设置失败") finally: cur.close() con.close() #该方法用于管理/增加用户角色关联表里面的内容 def add_user_role(self): print("用户可以选择的角色:1.第一类员工2.第一类员工的经理3.第二类员工4.第二类员工经理5.老板") user_type = int(input("请输入用户对应的角色id:")) if user_type == 1: user_role = "第一类员工" role_id = 101 return user_role,role_id elif user_type == 2: user_role = "第一类员工的经理" role_id = 100 return user_role,role_id elif user_type == 3: user_role = "第二类员工" role_id = 201 return user_role,role_id elif user_type == 4: user_role = "第二类员工的经理" role_id = 200 return user_role,role_id elif user_type == 5: print("无权限添加老板") return None,None else: print("无法识别用户对应的角色id,请按照上面输入用户角色对应的数字") return None,None #该方法用来展示输入要添加的用户的用户名以及对应你id def user_info(self): user_name=input('请输入用户名:') user_id=int(input('请输入用户id:' )) return user_name,user_id #该方法用来实现添加对应的用户 def add_user(self): (user_role,role_id)=self.add_user_role() if not user_role and not role_id : print("操作失败!") return (user_name,user_id)=self.user_info() con=sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db") cur=con.cursor() con.row_factory=sqlite3.Row try: #首先需要判断输入的用户名是否已经存在 sql='select *from user' cur.execute(sql) #判断输入的用户名是否在用户表当中 exist = False for user in cur: if user[1] == user_name: exist = True #此时,用户表中存在对应的用户 true_user_id=user[2] true_role_id=None #之后,从用户角色关联表当中查到对应的角色 sql1='select *from user_role' cur.execute(sql1) for row in cur: if row[1] == true_user_id: true_role_id = row[2] #此时,已经找到了在用户角色关联表当中的角色id #之后需要进行角色互斥,在这里面所有角色都为互斥,比如不可能既是老板又是员工,设定一个人只能拥有一个角色 if role_id == true_role_id: print("该用户已经存在这种角色") if not exist: #如果不在用户表中,需要把新的用户以及用户id添加到用户表当中 try: sql = 'insert into user(user_name,user_id) values(?,?)' cur.execute(sql,(user_name,user_id)) con.commit() print("新增用户成功") except Exception as e: print(e) con.rollback() print("新增用户失败") #之后,我们需要根据add_user_role()得知想要添加的用户对应的角色id,加到用户角色关联表当中 try: sql1 = 'insert into user_role(user_id,role_id) values(?,?)' cur.execute(sql1,(user_id,role_id)) con.commit() print("新增用户角色关联条目成功") except Exception as e: print(e) con.rollback() print("新增用户角色关联条目失败") except Exception as e: print(e) print("add_user()失败,请进行检查") finally: cur.close() con.close() def user_name_show(self): con = sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db") cur=con.cursor() con.row_factory=sqlite3.Row sql='select *from user' try: cur.execute(sql) print("显示用户信息") user_list=[] for row in cur: user_list.append(row[1]) print(user_list) except Exception as e: print(e) con.rollback() print("显示用户信息失败") finally: cur.close() con.close()对权限进行管理的类rolemanager()
包含的方法以及各自作用:
首先明确在这个类里面,我们首先要实现把具体例子的角色表以及对应的角色权限关联表初始化,其次要完成的是基于角色的权限的修改,在这里我是进行来一个限制,不能让一些角色通过提升或者删除权限来变成了另一个角色,最后的话是用来展示当前角色表信息的函数
- 对于角色表以及对应的角色权限关联表初始化的函数
def set_role_table(self):
#set the connection to the db file
con = sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db")
cur = con.cursor()
#creat the table
sql = 'insert into role(role_name, role_id) values(?,?)'
#execute
try:
cur.executemany(sql,[("第一类员工的经理",100),("第一类员工",101),("第二类员工的经理",200),("第二类员工",201),("Boss",404)])
#commitment
con.commit()
print("设置角色成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("设置角色失败")
finally:
#close the connect
cur.close()
con.close()
def set_role_permission_table(self):#设置对应的角色权限关联表
con = sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db")
cur = con.cursor()
sql='insert into role_permission(role_id,permission_id) values(?,?)'
try:
cur.executemany(sql,[(101,1002),(101,1003),(100,1002),(100,1003),(100,1005),(201,1001),(201,1002),(201,1004),(200,1001),(200,1002),(200,1004),(200,1005),(404,1001),(404,1002),(404,1003),(404,1004),(404,1005)])
con.commit()
print("角色权限关联表设置成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("角色权限关联表设置失败")
finally:
cur.close()
con.close()- 之后是对于权限的修改的函数,增加权限的时候要先判断该角色是否已经有了这个权限,二在删除的时候也应该先看是否具有这个权限,同时不能因为权限改变而改变身份,比如一类员工不能增加权限5,否则会变成第一类员工的经理
def modify_permission(self):
#set the connection to the db file
con = sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db")
cur = con.cursor()
#we need to modify the seperate data row, achieve this by using row
print("here is the id and the name:第一类员工:101 第一类员工的经理:100 第二类员工:201 第二类员工的经理:200 Boss:404")
con.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
print("do not modify the Boss's permission!!!")
role_id = int(input("请输入您要修改权限的角色对应的角色id:"))
addel = int(input("对该角色增加权限请输入1,删除权限请输入2:"))
print("所有可以增加或删除的权限:1001:新建 1002:读取 1003:执行 1004:更改 1005:删除")
if addel == 1:#when it comes to add permission
permission = int(input("请输入要增加权限的对应数字:"))
#then we need to check weather the permission is already exist
exist = False
#we need to check the permission that the role already have
permissionlist = []
#we need to check the role_permission table
sql = 'select *from role_permission'
cur.execute(sql)
for row in cur:
if row[1] == role_id:
permissionlist.append(row[2])
if row[2] == permission:
exist = True
print("该角色已经有了输入的permission id对应的权限,不需要进行增加")
#if the permission is not exist, add the permission to the role
if exist == False:
#之后我们需要实现对于权限的控制,不能是因为提升权限而变成了另一个角色
result = False
if role_id == 101:
if permission == 1005:
result = True
print("增加权限失败,因为第一类员工不能增加权限5,否则会变成第一类员工的经理")
cur.close()
con.close()
if role_id == 201:
if permission == 1005:
result = True
print("增加权限失败,因为第二类员工不能增加权限5,否则会变成第二类员工的经理")
cur.close()
con.close()
if role_id == 200:
if permission == 1003:
result = True
print("增加权限失败,因为第二类员工的经理不能增加权限3,否则会变成Boss")
cur.close()
con.close()
if role_id == 404:
result = True
print("Boss拥有所有权限,无法提升")
cur.close()
con.close()
if not result:
try:
sql1 = 'insert into role_permission(role_id,permission_id) values(?,?)'
cur.execute(sql1,(role_id,permission))
con.commit()
print("增加权限成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("增加权限失败,请进行检查")
finally:
cur.close()
con.close()
if addel == 2:#当要删除权限的时候
permission = int(input("请输入要删除权限的对应数字:"))
exist = False
sql = 'select *from role_permission'
permissionlist = []
cur.execute(sql)
for row in cur:
if row[1]==role_id:
permissionlist.append(row[2])
if row[2] == permission:
exist = True
print("检查通过,该角色拥有对应的权限,可以进行权限的删除")
result = False
if role_id == 100:
if permission == 1005:
result = True
print("删除权限失败,因为第一类员工的经理不能删除权限5,否则会变成第一类员工")
cur.close()
con.close()
if role_id == 200:
if permission == 1005:
result = True
print("删除权限失败,因为第二类员工的经理不能删除权限5,否则会变成第二类员工")
cur.close()
con.close()
if role_id == 404:
print("Boss拥有所有权限,不能删除Boss权限")
cur.close()
con.close()
if not result:
try:
sql1='delete from role_permission where pno=?'
cur.execute(sql1,(row[0],))
con.commit()
print("删除权限成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("删除权限失败")
finally:
cur.close()
con.close()
break
if not exist:
print("没有此权限")
cur.close()
con.close()至于用来展示的role_show()函数,和前面类的展示函数并没有什么区别
对于权限管理的类permissionmanager()
在这里重要的也就是对于权限表的管理,其他的调整关联表的函数上面已经实现
class permissionmanager():
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def permission_show(self):
con=sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db")
cur=con.cursor()
sql='select *from permission'
print('权限及权限id:')
try:
cur.execute(sql)
for permission in cur:
print(permission)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("显示权限信息失败")
finally:
cur.close()
con.close()
#设置对应的表
def set_permission_table(self):
con=sqlite3.connect("d:/Information System Security/RBAC/datatable.db")
cur=con.cursor()
sql='insert into permission(permission_name,permission_id) values(?,?)'
try:
cur.executemany(sql,[('新建',1001),('读取',1002),('执行',1003),('更改',1004),('删除',1005)])
con.commit()
print('权限表设置成功')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print('权限表设置失败')
finally:
cur.close()
con.close()最后是调用并且实例化上面类的主函数/文件main.py
在这里面主要是mian函数来调用其他类里面的方法,还有就是通过user_list()以及check()方法来访问用户表以及查询用户有没有对应的一些权限,以及最开始建立5个表的格式
在这里只贴出部分代码,具体的可以看py文件
def user_list():
con = sqlite3.connect("datatable.db")
cur = con.cursor()
con.row_factory=sqlite3.Row
sql='select *from user'
#进行查找
try:
cur.execute(sql)
for row in cur:
print(row[0],row[1],row[2])
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print('查询用户失败')
finally:
cur.close()
con.close()
def check(username, permission):
user_id = None
permission_id = None
role_id = None
permission_list = []
result = False #判断是否存在
con=sqlite3.connect("datatable.db")
cur=con.cursor()
con.row_factory=sqlite3.Row
#首先先查找对应的user_id
try:
sql='select *from user'
cur.execute(sql)
for row in cur:
if username == row[1]:
#找到对应的user_id
result = True
user_id = row[2]
if not result:
print("没有查到该username对应的user_id,请检查后再进行查询")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print('check():user_id查询失败,请检查code')
#之后来查询对应的role_id
try:
sql='select *from user_role'
cur.execute(sql)
for row in cur:
if user_id == row[1]:
role_id = row[2]
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("check():role_id查询失败,请检查code")
#之后查找所拥有的权限
try:
sql='select *from role_permission'
cur.execute(sql)
for row in cur:
if role_id == row[1]:
permission_list.append(row[2])
if not permission_list:
print('username对应的权限查询失败')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("check():role_permission查询失败,请检查code")
#最后查询对应的权限的id
try:
sql='select *from permission'
cur.execute(sql)
for row in cur:
if permission == row[1]:
permission_id = row[2]
if not permission_id:
print("permission对应的permission_id查询失败")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("check():role_id查询失败,请检查code")
#看输入的权限与查询出来的是否对应
try:
result2 = False
for i in permission_list:
if i == permission_id:
result2 = True
print("有此权限")
if not result2:
print("没有此权限")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
con.rollback()
print("check():权限不匹配,请检查code")
finally:
cur.close()
con.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
creat_table()
user_manage = usermanager()
role_manage = rolemanager()
permission_manage = permissionmanager()
user_manage.set_user_table()
role_manage.set_role_table()
permission_manage.set_permission_table()
user_manage.set_user_role_table()
role_manage.set_role_permission_table()
user_list()
user_manage.user_name_show()
role_manage.role_show()
permission_manage.permission_show()
permit = int(input("#####请输入你的身份:1.非管理员 2.管理员:#####"))
if permit == 2:
password = input("###请输入管理员账户密码:###")
if password == '1234':
print("1:显示当前信息 2:查询用户对应权限 3:添加用户 4:角色权限修改 5:退出")
while True:
option = int(input("请输入要进行的操作对应的数字"))
if option == 1:
user_manage.user_name_show()
role_manage.role_show()
permission_manage.permission_show()
elif option == 2:
username = input("请输入要查询的用户名:")
user_permission = input("请输入要查询该用户的权限(新建/读取/执行/更改/删除):")
check(username,user_permission)
elif option == 3:
user_manage.add_user()
elif option == 4:
role_manage.modify_permission()
elif option == 5:
break
else:
print("输入指令错误,请按照上面显示内容输入")
else:
print("密码错误,在运行中为方便使用,密码为1234")
if permit == 1:
print('1:展示当前信息 2:查询用户权限 3:退出')
while True:
option = int(input("请输入要进行的操作对应的数字"))
if option == 1:
user_manage.user_name_show()
role_manage.role_show()
permission_manage.permission_show()
elif option == 2:
username = input("请输入要查询的用户名:")
user_permission = input("请输入要查询该用户的权限(新建/读取/执行/更改/删除):")
check(username,user_permission)
elif option == 3:
break
else:
print("输入指令错误,请按照上面显示内容输入")
else:
print("输入指令错误,请按照上面显示内容输入")成果演示
运行对应的mian.py文件,可以看到如下内容
当为非管理员的时候,输入1,可以看到之后的可进行的操作,部分演示,在这里通过查询对应员工是否有权限可以来作为访问和访问拒绝的标志,有此权限说明对应用户可以进行访问,没有此权限则访问拒绝
之后当为管理员的时候,以添加用户为例子来看对应的运行结果
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!